List and Explain the Two Different Body Plans of Cnidarians
The polyp or tuliplike stalk form and the medusa or bell form. Cnidarias have an internal sac for digestion which is called the gastrovascular cavity.
Unit 5 2 Phylum Cnidaria The Biology Classroom
25How do Cnidarians eat.
. Cnidarians Medusa Cylindrical body arm-like tentacles mouth opens upward usually sessile Polyp Medusa bell shaped bottom mouth is at the bottom free-swimming structure fringe of tentacles that hang from the edge of the bell mouth opening located under the bell a gastrovascular. Purestock Getty Images. What do Cnidairnas eat.
Some species exhibit both body plans in their lifecycle. Two lesser-known groups are tiny moss-like creatures called hydroids and the ocean-going siphonophores. Examples of the polyp form are freshwater species of the genus Hydra.
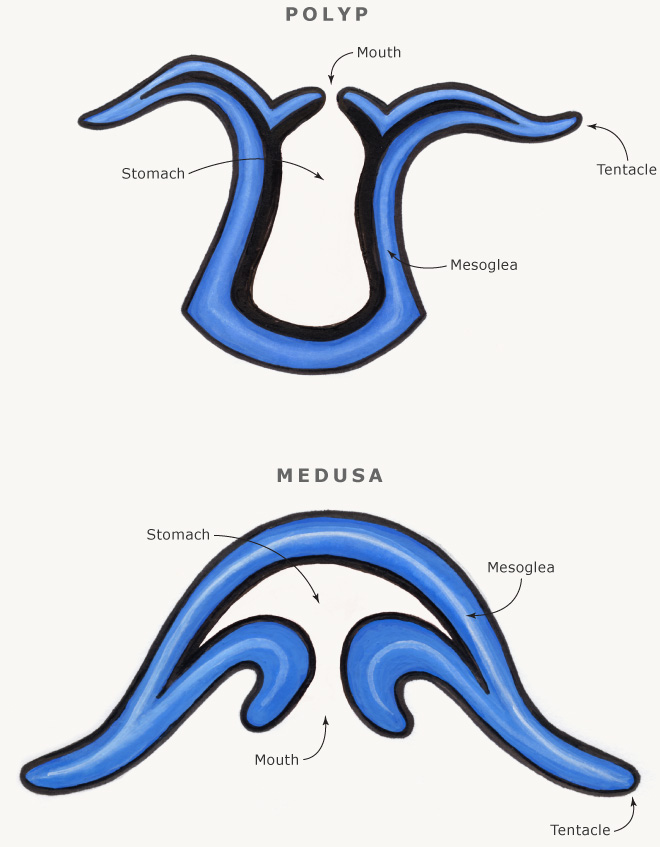
Figure 6 Cnidarian body forms Mouth Medusa. Label the cross-section of the two forms of Cnidarians. Cnidarians display two distinct body plans.
Tissues and digestive cavity. The polyp and the medusa. There are three major classes of Cnidarians.
Be sure to use the following terms in your description. Medusa - bell-shaped and free swimming. 26Describe the two basic body plans of Cnidarians.
Identify the two features of body plan that evolved with the cnidarians and ctenophores. They have nematocysts stinging cells. Polyp or stalk and medusa or bell.
Perhaps the best-known medusoid animals are the jellies jellyfish. The key characteristic features of cnidarians include radial symmetry acoelomate body with tissues lack of organs and the simple digestive sac that opens through a mouth which is surrounded by tentacles armed with nematocysts. Cnidarian is an animal species belonging to the Cnidarian phyla.
An individual with the polyp form is usually anchored to the substrate with. The phylum Cnidaria is made up of four classes. Corals sea anemones and jellyfish are the most familiar of the cnidarians.
An example of these is the hydra. Name and describe the other body form of cnidarians. Cnidarians consist of two cell layers.
Describe the two basic body plans of Cnidarians. Cnidarian Basics 18 Cnidarians are very diverse in form What is the common from BIOLOGY 101 at Holmes Community College. The midsagittal plane divides the body exactly in half into right and left portions.
Two distinct body plans are found in Cnidarians. Example - jellyfish float amond ocean currents. 2 Tissues The two body forms of cnidariansmedusa and polypconsist of the same body parts arranged differently.
Between both layers they have the mesoglea which is a connective layer. Tentacles radiate outward from the rim of the mouth. An example of the polyp form is found in the genus Hydra whereas the most typical form of medusa is found in the group called the sea jellies jellyfishPolyp forms are sessile as adults with a single opening the mouthanus to the digestive cavity facing up.
Cnidarians have two distinct morphological body plans known as polyp which are sessile as adults and medusa which are mobile. They are aquatic invertebrates mostly living in the ocean Pechenik 2000. Cnidarians as a whole have two body forms.
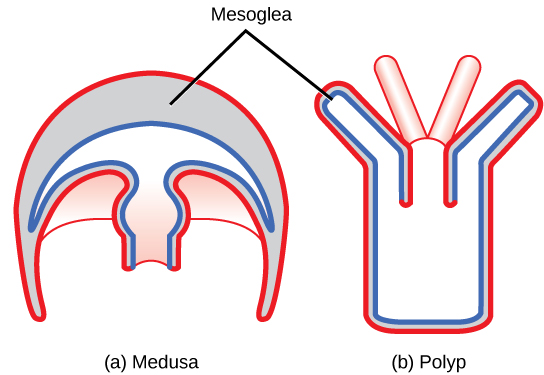
No cell is ever far from water. Between these is sandwiched the mesoglea a largely noncellular layer composed of a jellylike material permeated by a complex network of supporting fibres that may be microscopically thin or very thick. Polypoids are fixed.
Because the tentacles of corals jellyfish and sea anemones have this radial structure they can sting and capture food coming from any direction. Cnidarians do not have a transport system and the body surface is used for gaseous exchange. Explain how they are different from one another.
In addition to the two possible body forms all Cnidarians share certain common features. The cnidarian body plan is more complex than that of a spongeit contains specialized tissues that carry out particular functions. Hermaphroditic gamete spawn planktonic larvae.
The body systems that cnidarians have take two forms. Explain the significance of these features to their biological processes including locomotion body support reproduction and development. The epidermis and the gastrodermis.
Even though most of these organisms are marine creatures some are found in freshwater aquatic conditions. Explain how they are different from one another. The body plans cnidarians generally have radial symmetry Fig.
Describe the type of symmetry exhibited by Cnidarians. They have radial symmetry cutting planes through the center. Vertebrate animals have a number of defined body cavities as illustrated in Figure 8.
Many cnidarians take two main structural forms during their life cycles a polyp form and a medusa form. The two basic body plans of Cnidarians are polypoid and medusoid. Cnidarian also called coelenterate any member of the phylum Cnidaria Coelenterata a group made up of more than 9000 living species.
All cnidarians are carnivores and have very simple body structures adapted as predators. The fibres and jelly are elastic. Review and insert a picture of the cross-section of the two forms of Cnidarians.
An outer ectoderm and an inner endoderm the gastrodermis that lines the coelenteron. The main body forms are medusa and polyp. Siphonophores are colonies of highly specialised individuals.
Cnidarians have two cell layers. The tissues however are not organized into organs. Explain how they are different from one another.
Explain the process of reproduction in the sponge. All cnidarians have two membrane layers in the body. Describe the two basic body plans of Cnidarians.
First produce sperm and egg. The frontal plane divides the front and back and the transverse plane divides the body into upper and lower portions. Most of them live in.
Polyps are sessile as adults with a single opening to the digestive system the mouth facing up with tentacles. Two stages which include sexual and then asexual. The body wall of a cnidarian consists of three layers an outer.
Mostly marine animals the cnidarians include the corals hydras jellyfish Portuguese men-of-war sea anemones sea pens sea whips and sea fans. The gastrovascular cavity has only one opening a mouth through which the animal takes in food and releases waste. Describe the body PLAN.
The Hydrozoa the Scyphozoa and the Anthozoa.
Jellyfish And Other Cnidarians

Cnidarian Structure And Function Advanced Ck 12 Foundation

Polyp And Medusa Body Shapes Corals Anemones And Jellyfish Te Ara Encyclopedia Of New Zealand
No comments for "List and Explain the Two Different Body Plans of Cnidarians"
Post a Comment